Sep 21, 2023 5:10:15 PM
Picture this: You're driving down the highway, cruising in a car packed with cutting-edge technology that seamlessly connects you to the world.
Your vehicle isn't just a mode of transportation; it's a data hub, a guardian of safety, and a harbinger of the future.
Welcome to the world of Automotive Telematics, a realm where innovation knows no bounds.
In 2023, the telematics market was valued at a staggering USD 85.23 billion, and it shows no signs of slowing down.
With a projected CAGR of over ~17%, it's poised to soar to a mind-boggling USD 334.84 billion by 2032. Buckle up as we take you on a journey through the ever-changing paradigm of Automotive Telematics.
This shift is a result of telematics penetrating passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, off-highway vehicles, two wheelers, bicycles.
In addition to traditional emergency services, Telematics devices inside vehicles now serve as the digital nerve center, commonly known as the Data Gateway.
Forward-thinking OEMs have turned the telematics game on its head by introducing cutting-edge features. Your vehicle can now turn into a digital fortress, thanks to telematics.
Software Defined Vehicle (SDV) is another game changing concept that enables the vehicle software to keep updating periodically and provides users the best experience, performance and prevents possible security vulnerabilities.
Telematics services as backbone of Data Gateway with high speed 5G connectivity makes SDV a reality.
Let’s look at some of the key use cases for Telematics applications involving specific entities in the eco system:
Beyond these use cases, vehicle diagnostics emerge as the unsung heroes, tirelessly warding off potential hazards and glitches.
Think of it as your car's personal health tracker. Telematics services for remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance provide important insights directly to the user through a smartphone app.
Want to understand Telematics Ecosystem and role played by different players? Here’s your visual cue:
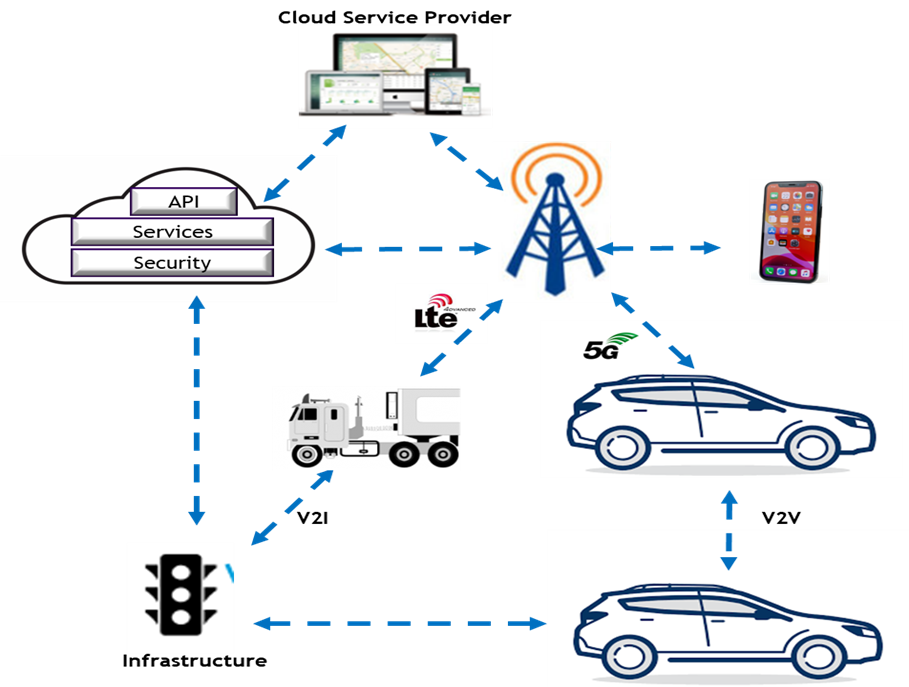
Telematics Cloud:
With the adoption of new technologies, changing vehicle architecture with Electric Vehicles and making vehicle always up-to-date with SW Update Over the Air (FOTA\SOTA\OTA), pushes changes in the Telematics Architecture:
Sep 21, 2023 5:10:15 PM
Picture this: You're driving down the highway, cruising in a car packed with cutting-edge technology that seamlessly connects you to the world.
Your vehicle isn't just a mode of transportation; it's a data hub, a guardian of safety, and a harbinger of the future.
Welcome to the world of Automotive Telematics, a realm where innovation knows no bounds.
In 2023, the telematics market was valued at a staggering USD 85.23 billion, and it shows no signs of slowing down.
With a projected CAGR of over ~17%, it's poised to soar to a mind-boggling USD 334.84 billion by 2032. Buckle up as we take you on a journey through the ever-changing paradigm of Automotive Telematics.
This shift is a result of telematics penetrating passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, off-highway vehicles, two wheelers, bicycles.
In addition to traditional emergency services, Telematics devices inside vehicles now serve as the digital nerve center, commonly known as the Data Gateway.
Forward-thinking OEMs have turned the telematics game on its head by introducing cutting-edge features. Your vehicle can now turn into a digital fortress, thanks to telematics.
Software Defined Vehicle (SDV) is another game changing concept that enables the vehicle software to keep updating periodically and provides users the best experience, performance and prevents possible security vulnerabilities.
Telematics services as backbone of Data Gateway with high speed 5G connectivity makes SDV a reality.
Let’s look at some of the key use cases for Telematics applications involving specific entities in the eco system:
Beyond these use cases, vehicle diagnostics emerge as the unsung heroes, tirelessly warding off potential hazards and glitches.
Think of it as your car's personal health tracker. Telematics services for remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance provide important insights directly to the user through a smartphone app.
Want to understand Telematics Ecosystem and role played by different players? Here’s your visual cue:

Telematics Cloud:
With the adoption of new technologies, changing vehicle architecture with Electric Vehicles and making vehicle always up-to-date with SW Update Over the Air (FOTA\SOTA\OTA), pushes changes in the Telematics Architecture: